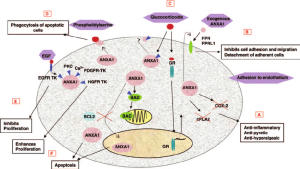
In a Translational research with bulk RNA sequencing analysis, scRNA-seq, and in vitro validation Hong Hu *et al.* from the Harbin Medical University published in the Journal: Discover Oncology to elucidate how methionine metabolism contributes to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment in gliomas, with a focus on macrophage polarization mediated by ANXA1. Elevated methionine metabolism in glioma cells correlates with higher WHO tumor grade and an immunosuppressive microenvironment. High methionine metabolic activity fosters M2 macrophage polarization via ANXA1, which is downregulated upon methionine deprivation 1).
Critical Review
This study leverages multi-omics datasets, particularly MMA-scoring and scRNA-seq, to draw a novel link between methionine metabolism and the immune suppressive phenotype in gliomas, focusing on macrophage polarization. The authors make a credible case for metabolic reprogramming as a driver of glioma malignancy. However, there are caveats:
– Strengths: The integration of bulk and single-cell RNA-seq enhances resolution, and the use of in vitro validation lends support to mechanistic claims. The correlation between MMA-scores and glioma grade is statistically compelling.
– Limitations: Despite the innovative premise, the study relies heavily on correlative data. Functional validation, particularly in vivo or using clinical samples, is lacking. The assertion that ANXA1-mediated macrophage polarization is solely Met-dependent needs further biochemical interrogation. Furthermore, patient sample heterogeneity and potential confounders are not adequately addressed.