Lumbar spinal stenosis classification
There is still no widely accepted diagnostic or classification criteria for the diagnosis of Lumbar spinal stenosis (LSS) and as a consequence studies use widely differing eligibility criteria that limit the generalizability of reported findings 1).
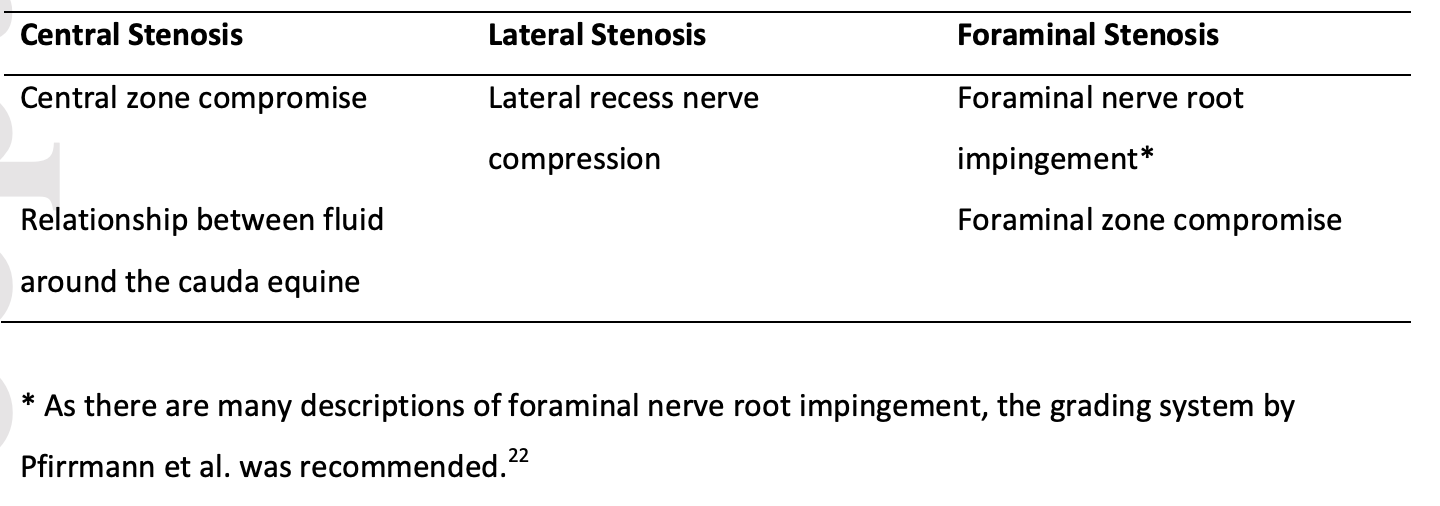
There are also no universally accepted radiographic definitions for the diagnosis of Lumbar central canal spinal stenosis, lumbar lateral recess stenosis and lumbar foraminal stenosis.
Three spinal canal morphologies were identified: (1) “flattened” canal with predominantly reduced spinal canal AP diameter, (2) spinal canal with predominantly reduced interlaminar angle, and (3) global reduction of all canal parameters. Early age at presentation and subtle spondylosis, although typical, should not be considered the identifying, differentiating factors 2).
Multi-level spinal stenosis
Lumbar central spinal canal stenosis
Lumbar foraminal stenosis
Lumbar lateral recess stenosis
Lumbar lateral recess stenosis
Congenital stenosis.
Degenerative stenosis.
Significant lumbar spinal stenosis and lower extremity arthritis may coexist in the elderly. This combination of lumbar stenosis with radiculopathy and lower extremity arthritis may lead to diagnostic uncertainty.