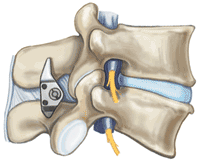
X-stop
Interspinous spacer used in the treatment of symptomatic lumbar spinal stenosis, show good result compared with nonoperative treatment, but showing higher reoperation rate than laminectomy.
2015
Lønne et al. published a prospective randomized controlled multicenter study.
To compare the effect of X-Stop with minimally invasive decompression (MID) in patients with neurogenic intermittent claudication due to lumbar spinal stenosis.
They enrolled 96 patients aged 50 to 85 years, with symptoms of neurogenic intermittent claudication within 250-m walking distance and 1- or 2-level lumbar spinal stenosis, randomized to either MID or X-Stop. Primary outcome was Zurich Claudication Questionnaire in this intention-to-treat analysis. Secondary outcome was Oswestry Disability Index, EuroQol 5-dimensional questionnaire, numerical rating scale 11 for lower back pain and leg pain, and risk for secondary surgery and complications.
No significant differences were found in Zurich Claudication Questionnaire between the groups at any follow-ups. Both groups had a statistical and clinical significant improvement at 6 weeks and throughout the 2-year observation period. The number of patients having secondary surgery due to persistent or recurrent symptoms was significantly higher in the X-Stop group, odds ratio (95% confidence interval) = 6.5 (1.3-31.9). Complication rate was similar and low, but more severe for MID.
Both MID and X-Stop led to significant symptom improvements. There were no significant clinical differences in effect between the methods at any of the follow-up time points. X-Stop had significant higher risk of secondary surgery. Complication was more severe for MID 1).
2013
The preliminary results of a prospective study of 40 patients at 1 year were published in 2007. The 2-year results of 57 patients are reported in this paper. Zucherman et al report 60% significant improvement at 1 year and 48.4% at 2 years.
Fifty-seven consecutive patients with radiologically confirmed lumbar spinal stenosis were enrolled and treated with the X-stop device. The device was implanted at a maximum of 2 affected levels. Clinical response was evaluated with the Zurich Claudication Questionnaire (ZCQ), Oswestry Disability Index, and Short Form-36 questionnaires preoperatively and 6, 12, and 24 months postoperatively.
Of the 57 patients enrolled, 54 completed the ZCQ questionnaire at 1 year and 46 patients at 2 years. Clinically significant improvement was attained by 65% at 1 year and 57% at 2 years and 70% were satisfied with the outcome of the surgery. Single level and double level insertions did not have significant difference in clinical outcome.
This study demonstrates with the use of ZCQ scores as primary outcome measures that improved clinical outcomes are maintained at 2 years after X-stop implantation 2).