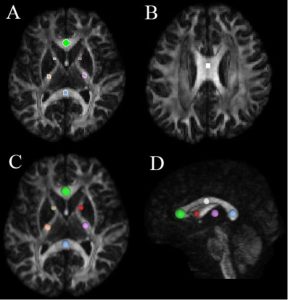
In a retrospective cohort Ishida *et al.* from the University hospitals—centres in Tokyo, (e.g., Tokyo Metropolitan Geriatric Center) published in the *Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging* to compare interstitial fluid volume fraction (Fint) and diffusivity (Dint), derived via spectral diffusion analysis, between idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) patients and healthy controls (HCs). In iNPH patients, spectral diffusion analysis revealed increased Fint and Dint in periventricular hyperintensity (PVH) regions of the centrum semiovale (CSO) and frontal white matter (FWM), while regions outside PVH did not differ from HCs 1).
Critical Review
* Strengths:
-
Utilizes advanced spectral diffusion with non‑negative least squares to separate Interstitial Fluid Dynamics an innovative approach.
-
Well‑defined region‑based ROI analysis including CSO, FWM, lenticular nucleus (LN).
-
Robust statistical treatment via Kruskal–Wallis with Dunn’s test; Spearman’s for correlations.
* Limitations & Concerns: