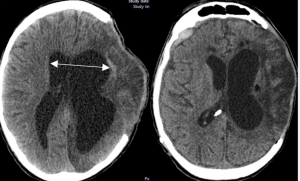
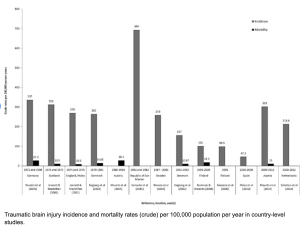
In a retrospective observational cohort study Romualdo et al. from the Department of Neurosurgery Faculty of Medicine, Technische Universität Dresden University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus published in the Neurosurgical Review to identify clinical, radiological, and surgical risk factors associated with the development of shunt-dependent posttraumatic hydrocephalus (PTH) in patients who underwent decompressive craniectomy following severe traumatic brain injury (TBI). Shunt-dependent post-traumatic hydrocephalus (PTH) occurred in 27% of patients after decompressive craniectomy for severe TBI. Independent risk factors included older age, basal cistern subarachnoid hemorrhage, post-traumatic ischemic infarcts, transcalvarial herniation, subdural hygroma, and progressive contusion hemorrhages. Surgical parameters were not predictive. Patients requiring shunt placement had significantly worse neurological outcomes 5).
🚨 The Illusion of Multidimensionality Despite claiming a “multidimensional” analysis, the study delivers a monotonous list of obvious associations—many of which have been reported in the literature for over a decade. Subarachnoid hemorrhage, infarction, hygroma, contusion progression… yes, thank you, we knew that. What’s new? Almost nothing.