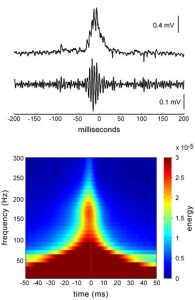
In a neurophysiological observational study Silva et al. from the Hospital Clínic–Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain published in Nature Communications to examine hippocampal and neocortical ripples during movie watching, and their relationship to event segmentation and later memory recall. The hippocampal ripples spike at event boundaries (linked to segmentation), while cortical ripples during events—especially in temporal cortex—predict later recall 1)
Critical Evaluation
Design & methods: – Intracranial recordings in ten epilepsy patients offer impressive temporal and spatial resolution in a naturalistic task. – However, sample size is small and patient population may limit generalizability. – Movie events are naturalistic, but segmentation boundaries may vary across subjects—analytical controls needed.
Results: – Clear increase in hippocampal ripples at event boundaries supports theories of hippocampal involvement in chunking continuous experiences. – Temporal cortex ripple rate correlation with recall is compelling—but causality is untested.
Limitations: – The patient sample’s neurological condition may alter ripple dynamics. – Lacking control comparisons (e.g., non-epileptic controls or different stimuli types). – Could benefit from linking neural dynamics more directly to behavioral performance (e.g., recall detailed metrics).