Interpeduncular cistern
see also Interpeduncular cistern hemorrhage.
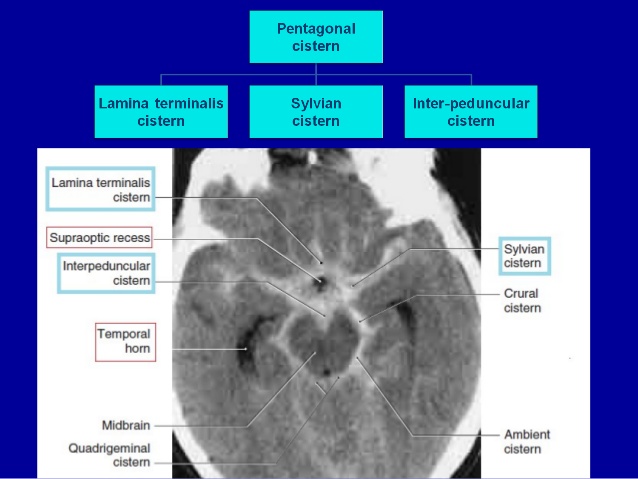 The interpeduncular cistern (basal cistern or Fossa interpeduncularis) is a wide cavity where the arachnoid extends across between the two temporal lobes.
The interpeduncular cistern (basal cistern or Fossa interpeduncularis) is a wide cavity where the arachnoid extends across between the two temporal lobes.
It encloses the cerebral peduncles and the structures contained in the interpeduncular fossa, and contains the arterial circle of Willis.
The optic chiasma
The bifurcation of the basilar artery.
Peduncular segments of the PICA.
Peduncular segments of the superior cerebellar arteries.
Perforating branches of the PICA.
The posterior communicating arteries (PCoA).
The basal vein of Rosenthal.
The third (III) cranial nerve, which passes between the posterior cerebral and superior cerebellar arteries.
Sufianov et al. studied the microsurgical anatomy of the interpeduncular cistern in 14 adult cadaver brains, using a surgical microscope(x3 to x40 magnification).
The interpeduncular cistern was divided into two portions: superficial (free) and deep (vascular). The superior wall of interpeduncular cistern was separated into the hypothalamic and mesencephalic part. It has communication with ambient cistern, prepontine cistern, carotid cistern, cerebellopontine cistern, oculomotor, and crural cisterns.
The interpeduncular cistern is a compound bulk structure. This classification is necessary for the quantitative and qualitative study of the interpeduncular anatomy. Also, it is necessary to neurosurgeons for the guiding line in this region 1).