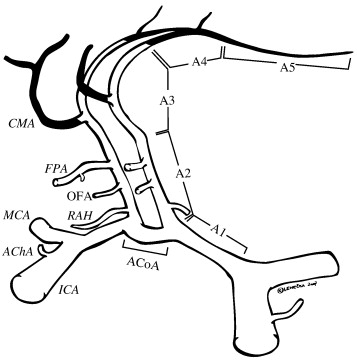
Anterior Cerebral Artery A3 segment
A3, also termed the pericallosal artery, is one of the (or the only) main terminal branches of the ACA, which extends posteriorly in the pericallosal sulcus to form the internal parietal arteries (superior, inferior) and the precuneal artery. This artery may form an anastomosis with the posterior cerebral artery.
The A3 segment is a frequent site of origin for the anterior, middle internal frontal, and callosomarginal artery.
A3 (precallosal): extends around the genu of the corpus callosum or distal to the origin of the callosomarginal artery, terminating where the artery turns directly posterior above the corpus callosum.
The pericallosal artery refers either to the distal part of the ACA starting from A2 (after the origin of the ACOM) or from A3 (defined after the origin of the callosomarginal artery). In the former case, the A2, A3, and A4-5 segments refer to proximal, middle, and distal segments of the pericallosal artery, respectively 1) 2).
Branches
A3
callosomarginal artery (runs in the cingulate sulcus)
Endo et al. report a case of a de novo aneurysm arising at the site of A3-A3 anastomosis. A 53-year-old woman underwent A3-A3 side-to-side anastomosis for the treatment of a ruptured right A2 dissecting aneurysm. At 44 months after surgery, a de novo aneurysm developed at the site of anastomosis. The aneurysm developed in the front wall of the anastomosis site, and projected to the anterosuperior direction. A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) study showed the localized region with high wall shear stress coincident with the pulsation in the front wall of the anastomosis site, where the aneurysm developed. A Y-shaped superficial temporal artery (STA) interposition graft was used successfully to reconstruct both ACAs, and then the aneurysm was trapped. To the authors' knowledge, this is the first case of a de novo aneurysm that developed at the site of an ACA-ACA side-to-side anastomosis. A CFD study showed that hemodynamic stress might be an underlying cause of the aneurysm formation. A Y-shaped STA interposition graft is a useful option to treat this aneurysm. Long-term follow-up is necessary to detect this rare complication after ACA-ACA anastomosis 3).