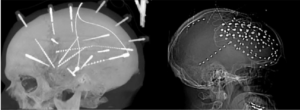
In a systematic review and metaanalysis of double‑arm comparative studies Bandopadhay et al. from the Houston Methodist Hospital published in the Journal of Neurosurgery to compare safety and seizure‑outcome profiles of stereoelectroencephalography (SEEG) vs. subdural electrodes (SDE) in pharmacoresistant epilepsy using quantitative double‑arm data SEEG demonstrated a higher rate of favorable seizure outcomes (RR 1.14, 95% CI 1.02–1.27; p=0.02) and lower complication rates overall (RR 0.49, 95% CI 0.37–0.66; p<0.00001). The benefit was significant in general adult cohorts but less pronounced in pediatric or older groups 1).
Critical Appraisal
* Strengths:
-
Restricting to double‑arm designs reduces cross‑study heterogeneity.
-
Large pooled cohort: 1,632 SEEG vs. 1,482 SDE patients.
-
Age‑stratified subgroup analysis adds nuance to applicability.
* Limitations:
-
Potential for publication bias—likely underreporting of negative or null comparative studies.