LINC01783
In vitro and in vivo molecular mechanistic investigations
Study Summary
Type of Study: In vitro and in vivo molecular mechanistic investigation First Author: Shaocai Hao et al. Author Affiliations:
-
Department of Neurosurgery, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
Journal: Biofactors DOI: 10.1002/biof.70029 PMID: 40546096 Publication Date: May–June 2025 Title: LINC01783 Promotes Glioma Tumorigenesis by Enhancing GATA3 Expression Through CBP-Mediated H3K27 Acetylation to Suppress PTEN Expression
Purpose
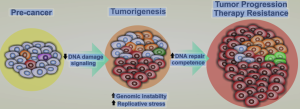
To elucidate the oncogenic function of the long intergenic non-coding RNA LINC01783 in glioma progression, focusing on its effect on GATA3 expression and PTEN suppression via CBP-mediated H3K27 acetylation.
Conclusions
LINC01783 is significantly upregulated in glioma tissues and enhances glioma progression by promoting GATA3 expression through CBP-mediated H3K27 acetylation. This, in turn, transcriptionally represses PTEN, contributing to increased tumor cell proliferation and stemness.
Critical Review
Methodological Weaknesses
-
Sample opacity: No clear details on glioma sample number, subtype stratification, or clinical metadata; undermines reproducibility and clinical significance.
-
In vivo data insufficiently controlled: No information on animal randomization, group sizes, or blinding procedures. Xenograft conclusions are weakly supported.
-
Epigenetic mechanistic oversimplification: Attribution of GATA3 regulation solely to CBP-H3K27ac is unconvincing; alternative pathways and compensatory mechanisms are unexamined.
-
Lack of causal proof: The PTEN axis is emphasized, but whether GATA3 mediates all observed phenotypes is not demonstrated.
-
No translational bridge: No therapeutic agent, inhibitor, or antisense strategy explored. The leap to “potential therapeutic target” is scientifically unfounded.