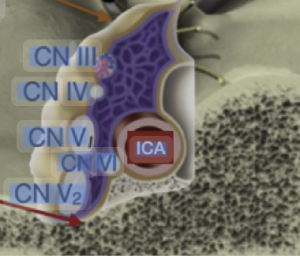
In a anatomic-imaging correlation study with a single-case MR + dissection design Mark el al. 1) from the Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, USA, Department of Neurosurgery, University of Valencia and Fundación Instituto Valenciano de Oncología (IVO), Valencia, Spain publiseh in the American Journal of Neuroradiology (AJNR) to determine whether high-resolution T2-weighted MRI can visualize the parasellar ligaments, which have previously only been described in cadaveric dissection or intraoperative findings, and to correlate these MRI findings with anatomical dissection in the same specimen. The authors report that parasellar ligaments can be identified on high-resolution T2-weighted MRI as T2-hypointense, bandlike structures originating from the medial wall of the cavernous sinus. They claim that identifying these ligaments may be relevant, given that resection of the medial wall of the cavernous sinus has been associated with better outcomes in functioning pituitary adenoma surgery.
This study is a prime example of technological overreach dressed up as discovery. It takes a single cadaver, applies ultra-high-resolution MRI, and then retrofits a minor fibrous band into a clinical “finding.” The result is a beautifully imaged, clinically irrelevant piece of anatomical embroidery that contributes nothing actionable to radiology, neurosurgery, or pituitary surgery.
❌ Critical Flaws