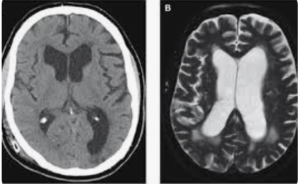
In a observational case-control (probable iNPH vs. age‑matched healthy controls), force‑plate COP analysis Park et al. from the Kyungpook National University, Daegu, South Korea published in the journal Neurology and therapy to quantify static postural control abnormalities in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus by assessing center‑of‑pressure (COP) metrics under eyes‑open and eyes‑closed conditions. Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus patients show significantly increased mediolateral sway and COP variability; anterior–posterior control is more vision‑dependent, suggesting direction‑specific balance deficits and potential for targeted rehabilitation 13).
In‑Depth Critique
* Scientific rigor:
-
Strengths: Objective force‑plate data; Bonferroni correction; clinically defined probable iNPH responding to CSFTT—a robust inclusion criterion.
-
Limitations: Modest sample size (56 iNPH vs 25 controls); cross‑sectional design precludes causality or post‑intervention implications.